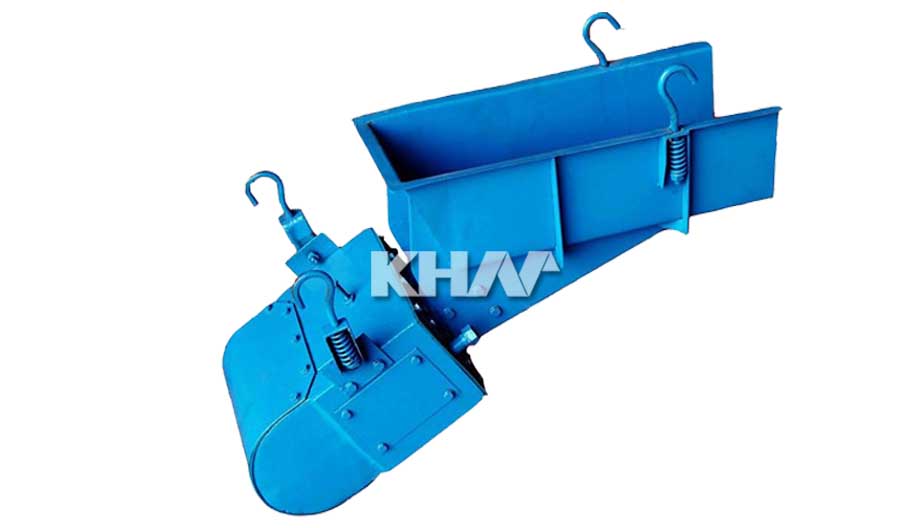

Electromagnetic Vibrating Feeder
Processing ability: 5–100 t/h
Feeding size: 50–150 mm
Power: 60–650 w
Voltage: 220 v
Applied material: powdery, granular materials, etc

Electromagnetic vibrating feeder uses the resonance principle of mechanical vibration and the double plastids work in the below critical and resonance state. The materials inside the material chute are continuously thrown up during the feeding process and move forwards along the track of a parabola. The control equipment of this series of electromagnetic vibrating feeder adopts silicon controlled half-wave rectification circuit, for this reason; during the using process, it can conveniently adjust the feeding amount through adjusting the silicon controlled open angle and realize centralized control and automatic control of the production flow.
Electromagnetic vibrating feeder is used for evenly and quantitatively feeding the materials from the storage bin or other storage machines to the material receiving equipment and it is the indispensable equipment to realize the automation of the line production. It is divided into open type and closed type. Our company can produce electromagnetic vibrating feeder, hopper and conveying machine according to the customers’ requirements.
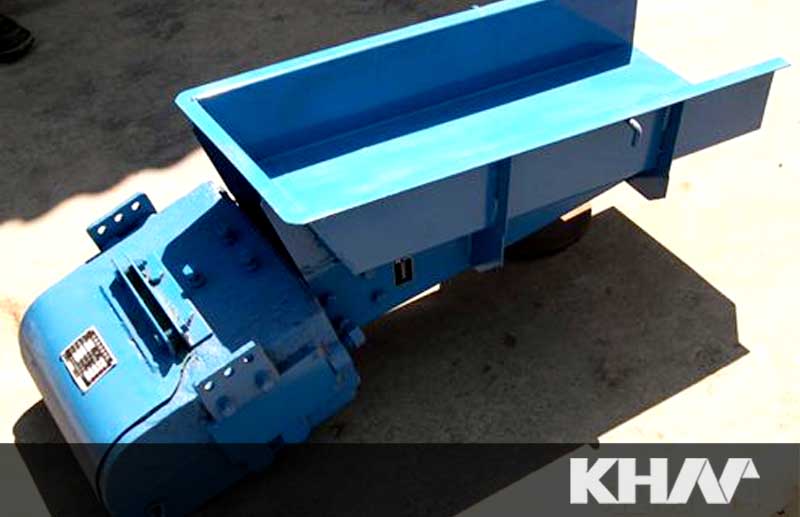

Small size, light weight, simple structure, convenient installation and maintenance and low operational fees.

Electromagnetic vibrating feeder uses the resonance principle of mechanical vibration and the double plastids work in the below critical and resonance state. The materials inside the material chute are continuously thrown up during the feeding process and move forwards along the track of a parabola. The control equipment of this series of electromagnetic vibrating feeder adopts silicon controlled half-wave rectification circuit, for this reason; during the using process, it can conveniently adjust the feeding amount through adjusting the silicon controlled open angle and realize centralized control and automatic control of the production flow.
|
Item
|
Feeding Capacity(t/h)
|
Max. Feeding Size(mm)
|
Power(w)
|
Voltage(v)
|
Current(a)
|
Double Amplitude(mm)
|
Gap(mm)
|
Total Weight(kg)
|
|
GZ1
|
5
|
50
|
60
|
220
|
1≤
|
1.75
|
1.9-2.2
|
75
|
|
GZ2
|
10
|
60
|
150
|
220
|
2.3≤
|
1.75
|
1.9-2.2
|
155
|
|
GZ3
|
25
|
70
|
200
|
220
|
3.8≤
|
1.75
|
1.9-2.2
|
225
|
|
GZ4
|
50
|
100
|
450
|
220
|
7≤
|
1.75
|
1.9-2.2
|
460
|
|
GZ5
|
100
|
150
|
650
|
220
|
10.6≤
|
1.75
|
1.9-2.2
|
656
|
